Table of Contents
Over 77,000 Internet-exposed IP addresses are vulnerable to the critical React2Shell remote code execution flaw (CVE-2025-55182), with researchers now confirming that attackers have already compromised over 30 organizations across multiple sectors.
React2Shell is an unauthenticated remote code execution vulnerability that can be exploited via a single HTTP request and affects all frameworks that implement React Server Components, including Next.js, which uses the same deserialization logic.
React disclosed the vulnerability on December 3, explaining that unsafe deserialization of client-controlled data inside React Server Components enables attackers to trigger remote, unauthenticated execution of arbitrary commands.
Developers are required to update React to the latest version, rebuild their applications, and then redeploy to fix the vulnerability.
On December 4, security researcher Maple3142 published a working proof-of-concept demonstrating remote command execution against unpatched servers. Soon after, scanning for the flaw accelerated as attackers and researchers began using the public exploit with automated tools.
Over 77,000 vulnerable IP addresses
Shadowserver Internet watchdog group now reports that it has detected 77,664 IP addresses vulnerable to the React2Shell flaw, with approximately 23,700 in the United States.
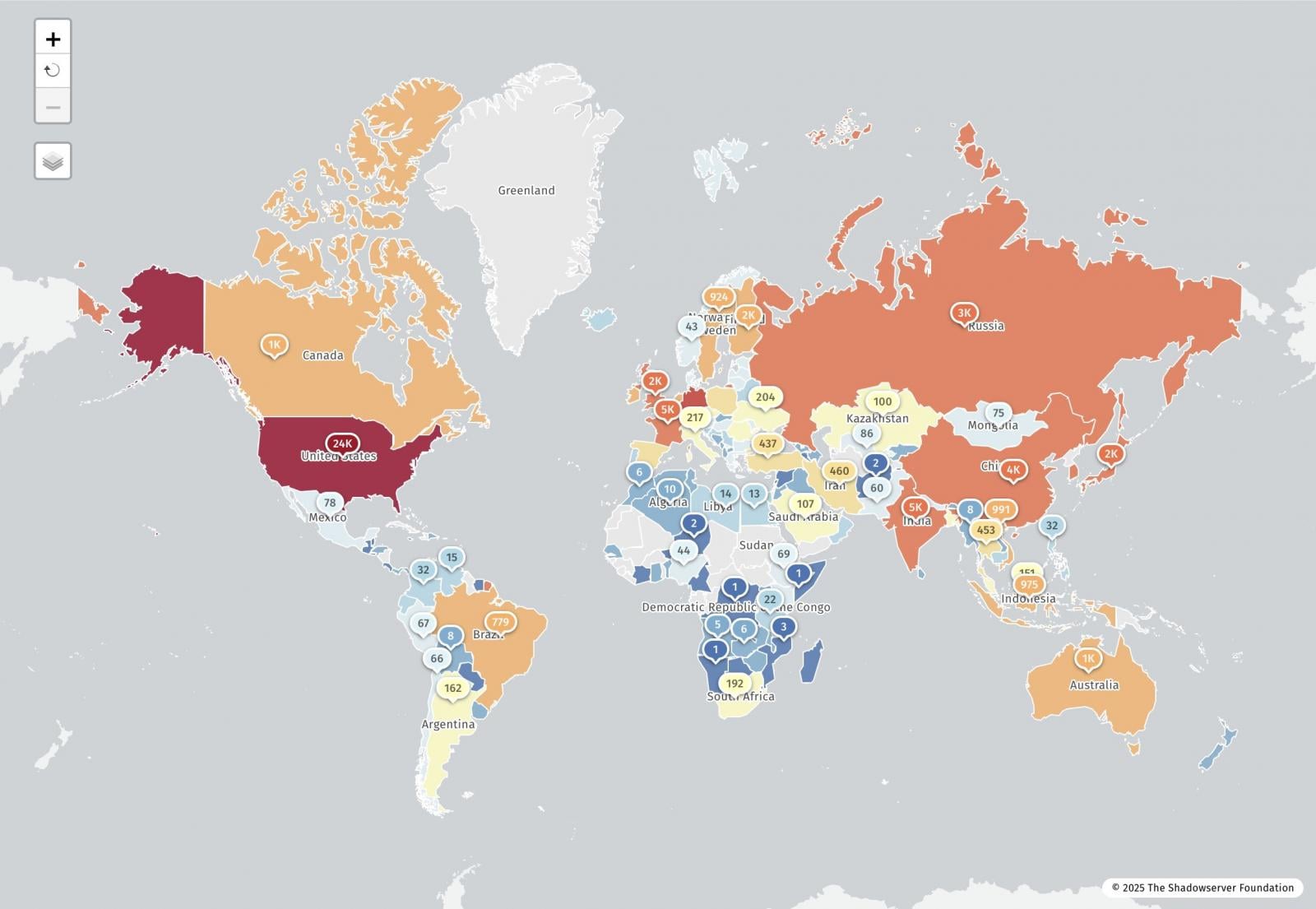
Source: ShadowServer
The researchers determined that IP addresses were vulnerable using a detection technique developed by Searchlight Cyber/Assetnote, where an HTTP request was sent to servers to exploit the flaw, and a specific response was checked to confirm whether a device was vulnerable.
GreyNoise also recorded 181 distinct IP addresses attempting to exploit the flaw over the past 24 hours, with most of the traffic appearing automated. The researchers say the scans are primarily originating from the Netherlands, China, the United States, Hong Kong, and a small number of other countries.
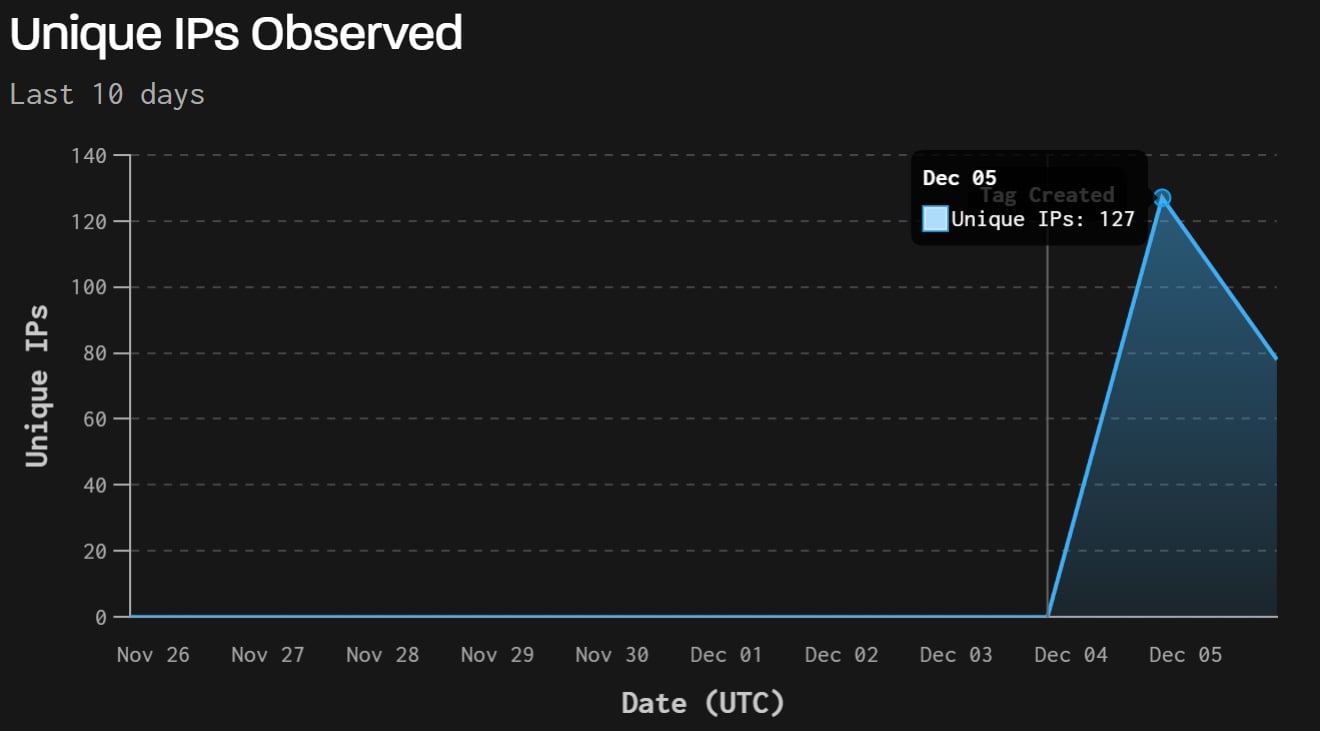
Source: Greynoise
Palo Alto Networks reports that more than 30 organizations have already been compromised through the React2Shell flaw, with attackers exploiting the vulnerability to run commands, conduct reconnaissance, and attempt to steal AWS configuration and credential files.
These compromises include intrusions linked to known state-associated Chinese threat actors.
Widespread exploitation of React2Shell
Since its disclosure, researchers and threat intelligence companies have observed widespread exploitation of the CVE-2025-55182 flaw.
GreyNoise reports that attackers frequently begin with PowerShell commands that perform a basic math function to confirm the device is vulnerable to the remote code execution flaw.
These tests return predictable results while leaving minimal signs of exploitation:
powershell -c "40138*41979"
powershell -c "40320*43488"
Once remote code execution was confirmed, attackers were seen executing base64-encoded PowerShell commands that download additional scripts directly into memory.
powershell -enc <base64>
One observed command executes a second-stage PowerShell script from the external site (23[.]235[.]188[.]3), which is used to disable AMSI to bypass endpoint security and deploy additional payloads.
According to VirusTotal, the PowerShell script observed by GreyNoise installs a Cobalt Strike beacon on the targeted device, giving threat actors a foothold on the network.
Amazon AWS threat intelligence teams also saw rapid exploitation hours after the disclosure of the React CVE-2025-55182 flaw, with infrastructure associated with China-linked APT hacking groups known as Earth Lamia and Jackpot Panda.
In this exploitation, the threat actors perform reconnaissance on vulnerable servers by using commands such as whoami and id, attempting to write files, and reading /etc/passwd.
Palo Alto Networks also observed similar exploitation, attributing some of it to UNC5174, a Chinese state-sponsored threat actor believed to be tied to the Chinese Ministry of State Security.
“Unit 42 observed threat activity we assess with high confidence is consistent with CL-STA-1015 (aka UNC5174), a group suspected to be an initial access broker with ties to the Chinese Ministry of State Security,” Justin Moore, Senior Manager at Palo Alto Networks Unit 42, told BleepingComputer via email.
“In this activity, we observed the deployment of Snowlight and Vshell malware, both highly consistent with Unit 42 knowledge of CL-STA-1015 (also known as UNC5174).”
The deployed malware in these attacks is:
- Snowlight: A malware dropper that allows remote attackers to drop additional payloads on breached devices.
- Vshell: A backdoor commonly used by Chinese hacking groups for remote access, post-exploitation activity, and to move laterally through a compromised network.
The rush to patch
Due to the severity of the React flaw, companies worldwide have rushed to install the patch and apply mitigations.
Yesterday, Cloudflare rolled out emergency detections and mitigations for the React flaw in its Web Application Firewall (WAF) due to its widespread exploitation and severity.
However, the update inadvertently caused an outage affecting numerous websites before the rules were corrected.
CISA has also added CVE-2025-55182 to the Known Exploited Vulnerabilities (KEV) catalog, requiring federal agencies to apply patches by December 26, 2025, under Binding Operational Directive 22-01.
Organizations using React Server Components or frameworks built on top of them are advised to apply updates immediately, rebuild and redeploy their applications, and review logs for signs of PowerShell or shell command execution.

Broken IAM isn’t just an IT problem – the impact ripples across your whole business.
This practical guide covers why traditional IAM practices fail to keep up with modern demands, examples of what “good” IAM looks like, and a simple checklist for building a scalable strategy.
